Architecture
The Leverege Platform provides a comprehensive web-based user interface that allows developers and system integrators to define data models, data processing pipelines, and customizable dashboards powered by real device data or simulated dataflows. The diagram below shows the high-level view of Leverege Platform.
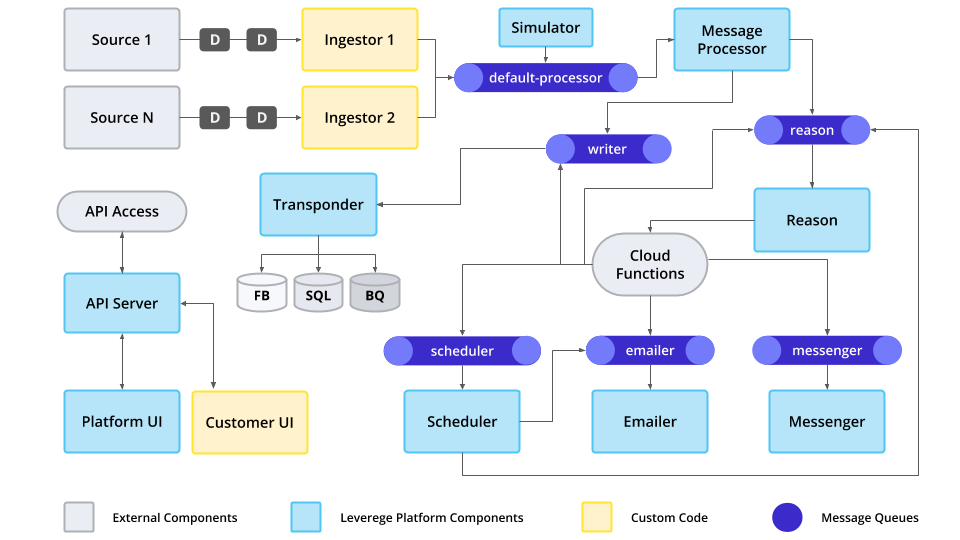
The Leverege Platform is built using a set of micro-services (services) that communicate via a message queueing system (like Google's PubSub or NSQ ) or, in some cases HTTP connections. Each service is a Docker image that is executed using Kubernetes, allowing them to be scaled up or down as needed. The queueing system works on the principle of a topic and a channel. When multiple readers of a queue have the same topic and channel, only one of them is notified with the message. This allows a service to scale horizontally when the number of messages increase. If two readers listen for messages on the same topic but with different channels, they will both receive the message.
The flow of data from a source device generally follows the following steps:
Data from source devices enter the system through either custom ingestion server or Rest Server. The ingestion server is a custom business logic server that knows how to talk to the data source. This includes managing the transport (HTTP, TCP, UDP, PubSub, etc) for the source and knowing how to parse the incoming data. The ingestion server will then publish an InboundDataEventMsg to the default-processor message topic. At this point the inbound msg only has a reference to the external name of the device: the network id, alias key, and value.
The Message Processor will receive this InboundDataEventMsg and attempt to resolve the external name (network id, alias key, and value) to an internal Device object. If the internal Device cannot be found, the message will be discarded. If the Device is found, the Message Processor will look up the routing steps for the message and send a DeviceDataEventMsg to the defined routes. By default, the message will be sent to the writer topic. If special business logic is needed, the message route for a Blueprint (or Device) can be configure to send the message to other topics such as a Reason script or custom topic.
By default the message is sent to the writer topic, which will be received by the Transponder service. Transponder will write the data to the current and historical databases.
If the message was also routed to a Reason script, that script may send out emails or SMS messages, or may schedule some action to occur at a later time.
Services
- API Server - Rest server that encompasses the core platform functionality
- Message Processor - Routes inbound messages
- Transponder - Writes data to databases
- Reason - Enables FaaS capabilities
- Scheduler - Creates, runs and maintains timers
- Messenger - Sends SMS messages
- Emailer - Sends emails
- Simulator - Simulates data being sent into the platform
- Rest-server - Generic ingestion service using HTTP
- DB-curator - Cleans old/stale data from the Databases
